Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamics Interactions between Andrographis paniculata, Andrographolide, and Oral Antidiabetic Drugs: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Evidence
Main Article Content
Abstract
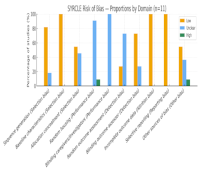
Herb–drug interactions between Andrographis paniculata, its constituent andrographolide, and oral antidiabetic drugs may alter drug exposure and glycemic responses. In this systematic review, we assessed the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics interactions between A. paniculata or andrographolide and oral antidiabetic drugs. We searched PubMed, Scopus, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, Web of Science, EBSCOhost, Portal Garuda, and other databases for articles published through August 2025. Search terms included free-text and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) keywords: “Herb–Drug Interactions,” andrographolide, Andrographis paniculata, and oral antidiabetic drugs (MeSH: Hypoglycemic Agents). Sixty-one records were identified; 10 preclinical reports were included, and no eligible human clinical studies were found. Heterogeneity in preparation type, dosing, and study design precluded meta-analysis; therefore, a narrative synthesis was performed. Across the included studies, combinations of A. paniculata or andrographolide with sulfonylureas often significantly increased drug exposure (maximum plasma concentration [Cmax]; area under the concentration–time curve [AUC]) and enhanced glucose-lowering. Repeated andrographolide dosing significantly reduced glipizide exposure and attenuated its effects. Tolbutamide exhibited pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamics dissociation, with significantly reduced exposure but preserved hypoglycemic activity. Saxagliptin exposure increased with reduced clearance; repaglinide showed higher Cmax and AUC with augmented glucose-lowering effects; metformin exhibited increased exposure with enhanced glycemic control; and acarbose showed no meaningful change. Overall, the findings suggest that A. paniculata and andrographolide potentiate the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamics effects of some oral antidiabetic drugs, whereas acarbose shows no interaction. Glipizide exhibits either synergistic or antagonistic effects depending on the preparation type. These context-dependent findings highlight the need for preparation-specific evaluation and clinical verification.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1.World Health Organization. Diabetes: Fact sheet. [Online]. 2024 [cited 2025 Sep 11]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
2.Pan HY, Wu LW, Wang PC, Chiu PH, Wang MT. Real-world evidence of the herb-drug interactions. J Food Drug Anal. 2022; 30(3):305-324. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.3428
3.World Health Organization. WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre (WHO GCTM) [Online]. 2024 [cited 2024 Jun 25]. Available from: https://www.who.int/initiatives/who-global-traditional-medicine-centre
4.Balkrishna A, Sharma N, Srivastava D, Kukreti A, Srivastava S, Arya V. Exploring the safety, efficacy, and bioactivity of herbal medicines: Bridging traditional wisdom and modern science in healthcare. Future Integr Med. 2024; 3(1):35-49. doi: 10.14218/FIM.2023.00086
5.Ekpor OS, Osei EP, Akyirem S. Use of traditional medicine among patients with diabetes mellitus in Africa: A systematic review. Int Health. 2024; 16(3):252-260. doi: 10.1093/inthealth/ihad080
6.Gupta RC, Chang D, Nammi S, Bensoussan A, Bilinski K, Roufogalis BD. Interactions between antidiabetic drugs and herbs: an overview of mechanisms and clinical evidence. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2017; 9(59):1-12. doi: 10.1186/s13098-017-0254-9
7.Alqathama A, Alluhiabi G, Baghdadi H, Aljahani L, Khan O, Jabal S, Makkawi S, Alhomoud F. Herbal medicine from the perspective of Type II diabetic patients and physicians: what is the relationship? BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020; 20(1):1-9. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-2854-4
8.Kifle ZD. Prevalence and correlates of complementary and alternative medicine use among diabetic patients in a resource-limited setting. Metabol Open. 2021; 10:100095. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100095
9.El Bayoumy, Dawod, W. Herbal Use and Perceptions among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Kuwait. J Diabetes Mellit. 2022; 12:50-62. doi: 10.4236/jdm.2022.121006
10.Thikekar AK, Thomas AB, Chitlange SS. Herb-drug interactions in diabetes mellitus: A review based on pre-clinical and clinical data. Phytother Res. 2021; 35(9):4763–4781. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7108
11.Kim J, Kwon M, Lee S, Noh J, Shim WS, Song E, Lee KT, Park JY, Yim SV, Kim BH. Comparisons of pharmacokinetics of glimepiride in combination with Ojeok-san versus glimepiride alone: an open-label, one-sequence, two-treatment controlled clinical study. Sci Rep. 2025; 15(1):25813. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09317-z
12.Babos MB, Redmond L, Herscu P. Herb–drug interactions: worlds intersect with the patient at the center. Medicines (Basel). 2021; 8(8):44. doi: 10.3390/medicines8080044
13.Okhuarobo A, Falodun JE, Erharuyi O, Imieje V, Falodun A, Langer P. Harnessing the medicinal properties of Andrographis paniculata for diseases and beyond: a review of its phytochemistry and pharmacology. Asian Pac J Trop Dis. 2014; 4(3):213-222. doi: 10.1016/S2222-1808(14)60509-0
14.Akhtar MT, Bin Mohd Sarib MS, Ismail IS, Abas F, Ismail A, Lajis NH, Shaari K. Anti-Diabetic Activity and Metabolic Changes Induced by Andrographis paniculata Plant Extract in Obese Diabetic Rats. Molecules. 2016; 21(8):1026. doi: 10.3390/molecules21081026
15.Pan, Y., Abd-Rashid, B.A., Ismail, Z. In vitro determination of the effect of Andrographis paniculata extracts and andrographolide on human hepatic cytochrome P450 activities. J Nat Med. 2011; 65:440-447. doi: 10.1007/s11418-011-0516-z
16.Pekthong D, Blanchard N, Abadie C, Bonet A, Heyd B, Mantion G, Berthelot A, Richert L, Martin H. Effects of Andrographis paniculata extract and Andrographolide on hepatic cytochrome P450 mRNA expression and monooxygenase activities after in vivo administration to rats and in vitro in rat and human hepatocyte cultures. Chem Biol Interact. 2009; 179(2-3):247-255. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2008.10.054
17.Qiu F, Hou XL, Takahashi K, Chen LX, Azuma J, Kang N. Andrographolide inhibits the expression and metabolic activity of cytochrome P450 3A4 in the modified Caco-2 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012; 141(2):709-713. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.002
18.Costello RA, Nicolas S, Shivkumar A. Sulfonylureas. [Updated 2023 Jul 12]. In: StatPearls [Online]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513225/
19.Jan A, Saeed M, Mothana RA. Association of CYP2C9*2 Allele with Sulphonylurea-Induced Hypoglycaemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Pharmacogenetic Study in Pakistani Pashtun Population. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(8):2282. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082282
20.Gong L, Goswami S, Giacomini KM, Altman RB, Klein TE. Metformin pathways: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2012; 22(11):820–827. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283559b22
21.Liang X, Giacomini KM. Transporters involved in metformin pharmacokinetics and treatment response. J Pharm Sci. 2017; 106(9):2245-2250. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.04.078
22.Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021; 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
23.Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016; 5:210. doi: 10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4
24.Hooijmans CR, Rovers MM, de Vries RB, Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, Wever KE. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014; 14:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-43
25.Campbell M, McKenzie JE, Sowden A, Katikireddi SV, Brennan SE, Ellis S, Hartmann-Boyce J, Ryan R, Shepperd S, Thomas J, Welch V, Thomson H. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: reporting guideline. BMJ. 2020; 368:l6890. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l6890
26.Samala S, Veeresham C. Andrographolide pretreatment enhances the bioavailability and hypoglycemic action of glimepiride and metformin. Int J Phytomed. 2015; 7(3):254-264.
27.Chen HW, Huang CS, Liu PF, Li CC, Chen CT, Liu CT, Chiang JR, Yao HT, Lii CK. Andrographis paniculata extract and andrographolide modulate the hepatic drug metabolism system and plasma tolbutamide concentrations in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013; 2013:982689. doi: 10.1155/2013/982689
28.Samala S, Veeresham C. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics interaction of boswellic acids and andrographolide with glyburide in diabetic rats: including its PK/PD modeling. Phytother Res. 2016; 30(3):496-502. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5556
29.Sari SP, Azizahwati A, Ratimanjari DA. Effect of Andrographis paniculata Nees herb infusion on the hypoglycemic activity of glibenclamide in diabetic male rats. Maj Ilm Kefarmasian. 2012; 9(1):1-11. doi: 10.7454/psr.v9i1.3359
30.Mouid MG. Effect of ethanolic extract of aerial parts of Andrographis paniculata on the pharmacokinetics of gliclazide in rats. Asian J Biomed Pharm Sci. 2015; 5(51):21-24. doi: 10.15272/ajbps.v5i51.755
31.Sundhani E, Nugroho AE, Nurrochmad A, Puspitasari I, Prihati DA, Lukitaningsih E. Pharmacokinetic herb-drug interactions of glipizide with Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) and andrographolide in normal and diabetic rats by validated HPLC method. Molecules. 2022; 27(20):6901. doi: 10.3390/molecules27206901
32.Syamsul ES, Nugroho AE, Pramono S. The antidiabetics of combination metformin and purified extract of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees in high fructose-fat fed rats. Tradit Med J. 2011; 16(3):124-132.
33.Nandru PK, Macha B, Yellu NR. Effect of andrographolide on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide in diabetic rats. Int J Pharm Biol Sci. 2022; 12(4):238-247. doi: 10.21276/ijpbs.2022.12.4.25
34.Wu S, Pan H, Huang Y. Pharmacokinetic interaction of saxagliptin with andrographolide and their hypoglycemic effect in type 2 diabetes rats. Acta Pol Pharm. 2023; 80(4):667-673. doi: 10.32383/appdr/17091
35.Sukmawati, Harsita MA, Kosman R. Hypoglycemic effect of the combination of Andrographis paniculata Nees leaf ethanol extract
and acarbose in alloxan-induced white rats. J Ilm As-Syifaa. 2016; 8(2):75-82. doi: 10.56711/jifa.v8i2.203
36.Sundhani E, Lukitaningsih E, Nurrochmad A, Nugroho AE. Potential pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics herb-drug interactions of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) and andrographolide: a systematic review. J Herbmed Pharmacol. 2022; 11(2):154-165. doi: 10.34172/jhp.2022.20
37.Saberi M, Ramazani Z, Rashidi H, Saberi A. The effect of CYP2C9 genotype variants in type 2 diabetes on the pharmacological effectiveness of sulfonylureas, diabetic retinopathy, and nephropathy. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2020; 16:241-248. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S230639
38.Mitchell SL, Leon DAC, Chaugai S, Kawai VK, Levinson RT, Wei WQ, Stein CM. Pharmacogenetics of hypoglycemia associated with sulfonylurea therapy in usual clinical care. Pharmacogenomics J. 2020; 20(6):831-839. doi: 10.1038/s41397-020-0171-4
39.Patel CG, Li L, Girgis S, Kornhauser DM, Frevert EU, Boulton DW. Two-way pharmacokinetic interaction studies between saxagliptin and cytochrome P450 substrates or inhibitors: simvastatin, diltiazem extended-release, and ketoconazole. Clin Pharmacol. 2011; 3:13-24. doi: 10.2147/cpaa.s15227
40.Boulton DW. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of saxagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017; 56(1):11–24. doi: 10.1007/s40262-016-0421-4
41.Mansour R, Borolossy R, Shaheen S, Sabri N. Evaluation of drug interactions of saxagliptin with sildenafil in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2022; 78(12):1935-1944. doi: 10.1007/s00228-022-03397-w
42.Intharuksa A, Arunotayanun W, Yooin W, Sirisa-ard P. A comprehensive review of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees and its constituents as potential lead compounds for COVID-19 drug discovery. Molecules. 2022; 27(14):4479. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144479
43.Health Canada. Summary Basis of Decision for Onglyza [Online]. Ottawa: Health Canada; 2025 [cited 2025 Nov 16]. Available from: https://dhpp.hpfb-dgpsa.ca/review-documents/resource/SBD00107
44.Tundis R, Patra JK, Bonesi M, Das S, Nath R, Talukdar AD, Das G, Loizzo MR. Anti-cancer agent: the labdane diterpenoid-andrographolide. Plants. 2023; 12(10):1969. doi: 10.3390/plants12101969
45.Bellanca CM, Augello E, Di Benedetto G, Burgaletto C, Cantone A, Cantarella G, Bernardini R. A web-based scoping review assessing the influence of smoking and smoking cessation on antidiabetic drug metabolism: implications for medication efficacy. Front Pharmacol. 2024; 15:1406860. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1406860
46.Guengerich FP. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes by drugs: molecular basis and practical applications. Biomol Ther. 2022; 30(1):1-18. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2021.102
47.Zaroug E, Albashir T, Arbab A, Mudawi M. Updates on the interactions of herbs constituents with cytochrome P450 drug metabolizing enzymes. Curr Enzyme Inhib. 2023; 19(3):167-178. doi: 10.2174/1573408019666230601121657
48.Li M, Wang Y, Chen Y, Dong L, Liu J, Dong Y, Yang Q, Cai W, Li Q, Peng B, Li Y, Weng X, Wang Y, Zhu X, Gong Z, Chen Y. A comprehensive review on pharmacokinetic mechanism of herb-herb/drug interactions in Chinese herbal formula. Pharmacol Ther. 2024; 264:108728. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108728
49.Bukowska B, Grzegorowska A, Szczerkowska-Majchrzak E, Bukowski K, Kadac-Czapska K, Grembecka M, Broncel M. Hazardous interactions between food, herbs, and drugs in the first stage of biotransformation: case reports of adverse drug interactions in humans. Int J Mol Sci. 2025; 26:5188. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115188
50.Pramesthi A, Lukitaningsih E, Nugroho AE. Potential pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PK–PD) drug-herbs interactions (DHI) from metformin and traditional medicines: a literature review. Pharmacogn J. 2022; 14(1):235-244. doi: 10.5530/pj.2022.14.29
51.Ailabouni AS, Singh DK, Thakur A, Paine MF, Boone EC, Gaedigk A, Prasad B. Quantitative contributions of hepatic and renal organic cation transporters to the clinical pharmacokinetic cimetidine-metformin interaction. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2025; 118(2):343-354. doi: 10.1002/cpt.3639
52.Yang Y, Zhang Z, Li P, Kong W, Liu X, Liu L. A whole-body physiologically based pharmacokinetic model characterizing interplay of OCTs and MATEs in intestine, liver and kidney to predict drug-drug interactions of metformin with perpetrators. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(5):698. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050698
53.Asano S, Galetin A, Tomita Y, Giacomini KM, Chu X, Yang X, Nakamura T, Kusuhara H, Sugiyama Y. Predicting OCT2/MATEs-mediated drug interactions in healthy volunteers and patients with chronic kidney disease: insights from extended clearance concept, endogenous biomarkers, and in vitro inhibition studies (perspectives from the International Transporter Consortium). Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2025; 118(5):994-1014. doi: 10.1002/cpt.3727
54.McIver LA, Preuss CV, Tripp J. Acarbose. [Updated 2023 Nov 13]. In: StatPearls [Online]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493214/
55.Elya B, Handayani R, Sauriasari R, Azizahwati A, Hasyyati U, Permana I, Yulinah E. Antidiabetic activity and phytochemical screening of extracts from Indonesian plants by inhibition of alpha amylase, alpha glucosidase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Pak J Biol Sci. 2015; 18(6):279-284. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2015.279.284
56.Ajayi OS, Balogun OS, Olawuni IJ, October N, Adigun R, Akinlade IG. Alpha amylase inhibition and antioxidant activities of bicyclic diterpenoid lactones from Andrographis paniculata. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2021; 5(6):1110-1117. doi: 10.26538/tjnpr/v5i6.22