Attenuating Effects of Rosmarinus officinalis Oil on Cadmium-altered Cognitive and Motor Abilities in Wistar Rat Models
Main Article Content
Abstract
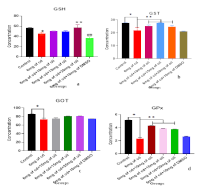
Cadmium (Cd) is one of the most dangerous environmental neurotoxins, linked to behavioural and cognitive impairments. This study examined whether Rosmarinus officinalis oil could reduce the effects of cadmium on cognitive and motor functions in Wistar rats. Forty-two male rats were divided into six groups of seven after two weeks of acclimation. Group 1 served as the control, Group 2 received 6 mg/kg of Cd, and Groups 3 to 5 received Cd along with rosemary oil at 10, 15, and 20 mg/kg, respectively. Group 6 received Cd and DMSO (10 mg/kg) as the solvent. The cadmium exposure and treatments lasted for 14 days. Anxiety, fear conditioning, motor activity, and memory were assessed with the open field test (OFT), Y-Maze, and elevated plus Maze (EPM). According to the results, group B had a memory deficit, decreased mobility, and increased fear. The preventive effects of rosemary oil were demonstrated by the improvement in behavioural outcomes (Figure 2). Specifically, Group 3 spent more time in the closed arms of the EPM and near the walls in the OFT (p < 0.05). Biochemical analysis revealed a significant decrease in reduced glutathione (GSH), while Glutathione S-transferase (GST) and Glutathione Oxaloacetate Transferase (GOT) levels increased markedly in group 2 (p<0.05). Histological analysis showed loss of nuclei, necrosis, and layer separation in tissues, as seen in Plates 1b and 2b, which were mitigated by rosemary oil (Plates 1c-f and 2c-f). Overall, rosemary oil has anti-inflammatory properties, which may potentially enhance memory and reduce anxiety.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1.Morales GB, Muñoz MA. Immune amnesia induced by measles and its effects on concurrent epidemics. J R Soc Interface. 2021;18(179):20210153. doi: 10.1098/rsif. 2021.0153.
2.Markowitsch HJ, Staniloiu A. Amnesic disorders. Lancet. 2012; 380(9851):1429-40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61304-4.
3.Marazzi C, Scoditti U, Ticinesi A, Nouvenne A, Pigna F, Guida L, Morelli I, Borghi L, Meschi T. Transient global amnesia. Acta Biomed. 2014; 85(3):229-35.
4.Vatansever D, Smallwood J, Jefferies E. Varying demands for cognitive control reveal shared neural processes supporting semantic and episodic memory retrieval. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):2134. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22443-2.
5.Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Exp Suppl. 2012; 101: 133-64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6.
6.Marini HR, Micali A, Squadrito G, Puzzolo D, Freni J, Antonuccio P, Minutoli L. Nutraceuticals: A New Challenge against Cadmium-Induced Testicular Injury. Nutrients. 2022; 14(3): 663. doi: 10.3390/nu14030663.
7.Uchewa OO, Chukwuemelie CE, Ovioson AI, Ibegbu AO. Alleviating Effects of Clove Essential Oil Disolved in Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) Against Cadmium-Induced Testicular and Epididymal Damages in Male Wistar Rats. Arch Razi Inst. 2023; 78(6): 1728-1737. doi: 10.32592/ARI.2023.78.6.1728.
8.Agnihotri SK, Agrawal U, Ghosh I. Brain most susceptible to cadmium-induced oxidative stress in mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2015; 30:184-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.12.008.
9.Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M, Hosseinzadeh H. Therapeutic effects of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its active constituents on nervous system disorders. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020; 23(9):1100-1112. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.45269.10541.
10.Ghasemzadeh RM, Hosseinzadeh H. Therapeutic effects of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its active constituents on nervous system disorders. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020; 23(9):1100-1112. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.45269.10541.
11.Gok Metin Z, Arikan Donmez A, Izgu N, Ozdemir L, Arslan IE. Aromatherapy Massage for Neuropathic Pain and Quality of Life in Diabetic Patients. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2017; 49(4):379-388. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12300.
12.Cui J, Li M, Wei Y, Li H, He X, Yang Q, Li Z, Duan J, Wu Z, Chen Q, Chen B, Li G, Ming X, Xiong L, Qin D. Inhalation Aromatherapy via Brain-Targeted Nasal Delivery: Natural Volatiles or Essential Oils on Mood Disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:860043. doi:10.3389/fphar. 2022.860043.
13.Moore J, Yousef M, Tsiani E. Anticancer Effects of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract and Rosemary Extract Polyphenols. Nutrients. 2016; 8(11):731. doi: 10.3390/nu8110731.
14.González-Vallinas M, Molina S, Vicente G, Zarza V, Martín-Hernández R, García-Risco MR, Fornari T, Reglero G, Ramírez de Molina A. Expression of microRNA-15b and the glycosyltransferase GCNT3 correlates with antitumor efficacy of Rosemary diterpenes in colon and pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 2014; 9(6): e98556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098556.
15.Kraeuter AK, Guest PC, Sarnyai Z. The Open Field Test for Measuring Locomotor Activity and Anxiety-Like Behavior. Methods Mol Biol. 2019; 1916:99-103.
16.Seibenhener ML, Wooten MC. Use of the Open Field Maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J Vis Exp. 2015; (96): e52434. doi: 10.3791/52434.
17.Sturman O, Germain PL, Bohacek J. Exploratory rearing: a context- and stress-sensitive behavior recorded in the open-field test. Stress. 2018; 21(5):443-452. doi: 10.1080/10253890.2018.1438405.
18.Hritcu L, Cioanca O, Hancianu M. Effects of lavender oil inhalation on improving scopolamine-induced spatial memory impairment in laboratory rats. Phytomedicine. 2012; 19(6):529-34. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.02.002.
19.Foyet HS, Abaïssou HH, Wado E, Acha EA, Alin C. Emilia coccinae (SIMS) G Extract improves memory impairment, cholinergic dysfunction, and oxidative stress damage in scopolamine-treated rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015; 15:333. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0864-4.
20.Walf AA & Frye CA. The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat Protoc. 2007; 2(2): 322-328. doi: 10.1038/nprot 2007.44.
21.Nieto G, Ros G, Castillo J. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis, L.): A Review. Medicines (Basel). 2018; 5(3): 98. doi: 10.3390/medicines5030098.
22.Otvos J. Measurement of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin Cardiol. 1999; 22(6 Suppl): II21-II27. doi: 10.1002/clc. 4960221405.
23.Erukainure OL, Ijomone OM, Sanni O, Aschner M, Islam MS. Type 2 diabetes induced oxidative brain injury involves altered cerebellar neuronal integrity and elemental distribution, and exacerbated Nrf2 expression: therapeutic potential of raffia palm (Raphia hookeri) wine. Metab Brain Dis 2019; 34:1385–1399. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11011-019-00444-X.
24.Wang H, Abel GM, Storm DR, Xia Z. Cadmium Exposure Impairs Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Toxicol Sci. 2019; 171(2):501-514. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz152.
25.Pulido G, Treviño S, Brambila E, Vázquez-Roque R, Moreno-Rodríguez A, Peña Rosas U, Moran-Perales JL, Handal Silva A, Guevara J, Flores G, Díaz A. The Administration of Cadmium for 2, 3, and 4 Months Causes a Loss of Recognition Memory, Promotes Neuronal Hypertrophy and Apoptosis in the Hippocampus of Rats. Neurochem Res. 2019; 44(2):485-497. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-02703-2.
26.Jan AT, Azam M, Siddiqui K, Ali A, Choi I, Haq QM. Heavy Metals and Human Health: Mechanistic Insight into Toxicity and Counter Defense System of Antioxidants. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(12):29592-29630. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226183.
27.Wolf U, Rapoport MJ, Schweizer TA. Evaluating the affective component of the cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009; 21(3):245-253. doi: 10.1176/jnp.2009.21.3.245.
28.Shimizu K, Matsubara K, Uezono T, Kimura K, Shiono H. Reduced dorsal hippocampal glutamate release significantly correlates with the spatial memory deficits produced by benzodiazepines and ethanol. Neuroscience. 1998; 83(3):701-706. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00339-4.
29.Kumar A, Pandey R, Siddiqi NJ, Sharma B. Oxidative stress biomarkers of cadmium toxicity in mammalian systems and their distinct ameliorative strategy. J Appl Biotechnol Bioeng. 2019; 6(3):126‒135. doi: 10.15406/jabb.2019.09.00184.
30.Kumar A, Khushboo, Pandey R, Sharma B. Modulation of Superoxide Dismutase Activity by Mercury, Lead, and Arsenic. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020; 196(2):654-661. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01957-3.
31.Aoyama K. Glutathione in the Brain. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(9):5010. doi: 10.3390/ijms22095010.
32.Gonçalves JF, Fiorenza AM, Spanevello RM, Mazzanti CM, Bochi GV, Antes FG, Stefanello N, Rubin MA, Dressler VL, Morsch VM, Schetinger MR. N-acetylcysteine prevents memory deficits, the decrease in acetylcholinesterase activity, and oxidative stress in rats exposed to cadmium. Chem Biol Interact. 2010; 186(1):53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.04.011.
33.Koehl M, Abrous DN. A new chapter in the field of memory: adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci. 2011; 33(6):1101-1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07609.x.
34.Enogieru AB, Inegbedion GO. Attenuation of Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Impairment in Cadmium Chloride-Exposed Wistar Rats Pre-treated with Ethanolic Turmeric Root Extract. J Phytopharmacol 2022; 11(2):118-124. doi: 10.31254/phyto.2022.11212.
35. Treviño S, Pulido G, Fuentes E, Handal-Silva A, Moreno-Rodríguez A, Venegas B, Flores G, Guevara J, Díaz A. Effect of cadmium administration on the antioxidant system and neuronal death in the hippocampus of rats. Synapse. 2022; 76(9-10): 1-16. doi: 10.1002/syn.22242.