Antidiabetic and Histopathological Effects of Two Herbal Formulations on Albino Wistar Rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
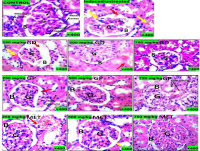
This study evaluated antidiabetic and histopathological effects of two herbal formulations ‘B-Gludecon’ and ‘B-Glupocon’ on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats (40 mg/kg/b.wt.). Sixty-six Wister albino rats were placed into eleven cages containing 6 rats per cage, and fasted for 12 hours before induction of diabetes. The diabetic rats in groups A-C were orally dosed daily with B-Gludecon for 10 days, and those in groups D-F were given B-Glupocon at 250, 500, and 750 mg/kg. Groups G-I rats had the standard drug Metformin at 250, 500, and 750 mg/kg oral doses, in contrast, groups J rats were diabetic without treatment (negative control) and group K rats received distilled water (positive control). The fasting blood sugar levels were determined at the intervals of 72 hours, 144 hours and 240 hours using the Accu-Check glucometer and recorded before sacrifice. The kidney and liver were harvested for histopathological analysis. The results showed that B-Gludecon and B-Glupocon at 500 mg/kg had better significant hypoglycemic effects than metformin (p ≤ 0.05), lowering the concentration of glucose in the blood by 83.24% and 88.22%, respectively. Histopathological analysis revealed that B-Glupocon was more potent in restoring the architectural distortions of the hepatic and renal tissues observed in the diabetic rats. Conclusively, these findings suggest that B-Glupocon and B-Gludecon may be useful in the prevention and treatment of diabetes, and further investigations are necessary to fully explore their therapeutic potential.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1.Ogunkunle ATJ, Ideh JE, Obiremi EO, Jimoh MA. An Investigation into the Practice and Perceived Essence of Medicinal Herb Authentication by Some Stakeholders of Traditional Medicine in Ogbomoso, Oyo State, Nigeria. Int J Tradit Nat Med 2019; 9(1): 17-30.
2.Huai H. Ethnomedicinal analysis of toxic plants from five ethnic groups in China. Ethnobot Res Appl 2010; 8: 169-179.
3.Husain SZ, Malik RN, Javaid M, Bibi S. Ethnobotanical properties and uses of Medicinal plants of Morgah Biodiversity Park, Rawalpindi. Pak J Bot 2008; 40(4): 1897-1911.
4.Adeghate E, Schattner P, Dunn E. An update on the etiology and epidemiology of diabetes mellitus. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006; 1084: 1-29.
5.Petchi RR, Parasuraman S, Vijaya C. Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects of an ethanolic extract of the whole plant of Tridax procumbens (Linn.) in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. J Basic Clin Pharm 2013; 4: 88-92.
6.Parasuraman S, Kumar E, Kumar A, Emerson S. Free radical scavenging property and diuretic effect of triglize, a polyherbal formulation in experimental models. J Pharmacol Pharmacother 2010; 1: 38-41.
7.Mandavi DC, Sachdev A, Tiwari P. Adverse drug reactions and their risk factors among Indian ambulatory elderly patients. Indian J Med Res 2012; 136(3): 404-410.
8.Liu X, Wei J, Tan F, Zhou S, Würthwein G, Rohdewald P. Antidiabetic effect of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes. Metab. 2010; 59(3): 285-292.
9.Khan A, Safdar M, Ali Khan MM, Khattak KN, Anderson RA. Cinnamon improves glucose and lipids of people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003; 26(12): 3215-3218.
10.Kim J, Lee Y, Kim B. Ginseng, a traditional herbal medicine, and its pharmacological effects. J Ginseng Res 2011; 35(2): 129-138.
11.Sharma P, Kumar P, Kumar A, Deshkar S. Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic activity of Gymnema sylvestre in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 2010; 62(8): 1092-1100.
12.Srinivasan K, Sathish S, Rajasekaran A. Antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of Curcuma longa extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 2018; 70(8): 1051-1063.
13.Arka JC, Tanvir MU, Uddin BM, Redwan MZ, Saikat M, Rajib D, Firzan N, Kuldeep D, Arpita R, Md. Jamal H, Ameer K, and Talha BE. Allium cepa: A Treasure of Bioactive Phytochemicals with Prospective Health Benefits. Hindawi Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022: 4586318.
14.Chisom FE, Asukwo AE, Uduak MW, Stephen OO, Churchill JI. Phytochemical Composition of Cassia alata Leaf Extract and its Effect on the Histology of the Pancreas of Diabetic Wistar Rats. IOSR J Pharm Bio Sci 2013; 5(5): 07-13.
15.Barnabe LN, Abiasse R, Kinyola MJ, Jean GS, Balthazar TT, Benjamin AT, Paul DDD, Sélestin DS, Pierre K. Antidiabetic and antiradical effects of Garcinia kola seed in Dexamethasone-induced hyperglycemic rats. Int J Adv Res Med 2022; 4(2): 108-117.
16.Ogunkunle ATJ, Oyelakin TM, Enitan AO, Oyewole FE. A Quantitative Documentation of the Composition of Two Powdered Herbal Formulation (Antimalaria and Haematinic) Using Ethnomedicinal Information from Ogbomoso, Nigeria. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 751291.
17.Abubakar AR, Mainul H. Preparation of Medicinal Plants: Basic extraction and fractionation procedures for experimental purposes. J Pharm Bioall Sci 2020; 12(3): 258-265.
18.Ajayi FA, Olorunisola OS, Adewale A, Olorunfemi FG, Abiodun OO, Adegbola PA, Afolabi OK. Anti-hyperglycemic and mode of action of Thaumatococcus danielli (BENN.) BENTH ethanol leave extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. AJRIMPS 2019; 6(2): 1-10.
19.Fongang FY, Bankeu KJ, Gabel ES, Iftikhar A, Lenta NB. Extraction of bioactive compounds from medicinal plants and herbs. In: Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Medicinal Plants and Herbs. IntechOpen; 2021.
20.Umpierrez GE, Korytkowski M. Diabetic emergencies – ketoacidosis, hyperglycaemic hyperosmolar state and hypoglycaemic. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2013; 9(10): 597-606
21.Rajendran RP, Chockalingam V, Subramani P. Antidiabetic activity of polyherbal formulation in Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide induced diabetic Wistar rats. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2014; 4(2): 108-117.
22.Eyo JE, Ozougwu JC, Echi PC. Hypoglycemic effect of Allium cepa, Allium sativum and Zingiber officinale aqueous extracts on alloxan induced diabetic Rattus norvegicus. Med. J. Islamic World Acad. Sci. 2011; 19:3, 121-126
23.Suksanga A, Sunisa S, Chutha T. The potential antidiabetic properties of Liang (Gnetum gnemon var. tenerum) leaves. Food Sci Technol Campinas 2022; 42: e64522.
24.Naowaboot J, Piyabhan P. Erratum to: Senna alata leaf extract restores insulin sensitivity in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Clin Phytosci 2016; 2(1): 1-9.
25.Alvarez-cilleros D, Martin MN, Ramosis. Epicatechin and the colonic 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid Metabolite Regulate Glucose Uptake, Glucose Production and Improve Insulin Signaling in Renal NRK-52E Cell. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018; 62(2): 1700470.
26.Komers R, Oyama TT, Beard DR, Tikellis C, Xu B, Lotspeich DF, Anderson S. Rho kinase inhibition protects kidneys from diabetic nephropathy without reducing blood pressure. Kidney Int 2011; 79(4): 432-442.
27.Ortega-Martinez M, Gutierrez-Davila V, Gutierrez-Arenas E, Niderhauser-Garcia A, Cerda-Flores RM, Jaramillo-Rangel G. The Convoluted Tubules of the Nephron Must Be Considered Elliptical, and Not Circular, in Stereological Studies of the Kidney. Kidney Blood Press Res 2021; 46(2): 229-235.
28.Rinalda C, Nugroho TE, Batubara L, Budiastuti A. Melatonin Can Not Significantly Reduce Blood Sugar Levels. Diponegoro Med J 2021; 10(4): 234-240.
29.Safaet AM, Moklesur RS, Taposhi NS, Md. Nafees RC, Mohammad AR, Nusrat IC, Chao Z, Jianbo X, Elsayed EH, Shah AK, Isa NM. Antidiabetic Phytochemicals from Medicinal Plants: Prospective Candidates for New Drug Discovery and Development. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022; 13: 800714
30.Bain SC. The Cellnovo Insulin Delivery System. Eur. Endocrinol. 2017; 13(01): 13–18.
31.Imieje VO, Onochie CF, Nwaka B, Falodun A. In vitro Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potentials of Extracts of the Stem Bark of Cylicodiscus gabunensis (Harms) Mimosaceae. Trop J Nat Prod Res, 2022; 6(11):1858-1863.
32.Fitriana N, Yustisia I, Kadir S, Azis I, Hardjo M. Effect of Papaya Peel Nata Oral Administration on the Blood Glucose Level in Male Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mellitus. Trop J Nat Prod Res, 2025; 9(3): 1058 – 1066.