Protective Effect of Jatropha tanjorensis Leaves Ethanol Extract on Testosterone-Induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Albino Rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
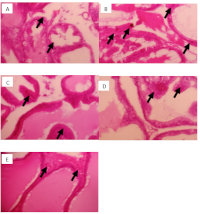
This study examined the protective effect of Jatropha tanjorensis leaves ethanol extract (JTLEE) on testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in albino rats. Twenty-five (25) male rats were employed for the study. Five (5) groups of five (5) rats each were created from the animals. Group 1 was neither induced nor treated (normal control), Group 2 was induced but not treated (untreated control), Group 3 was induced and treated with 1 mg/kg b.w. of finasteride (standard control). Groups 4 and 5 were induced and treated with 100 and 200 mg/kg of JTLEE (low and high dose), respectively. The BPH model was developed in the rats (groups 2 to 5) by subcutaneous injection of testosterone propionate (5 mg/kg body weight (b.w)) for 21 days. The JTLEE-treated groups showed a significant (p < 0.05) decrease in the weight of the prostate, bladder, and prostate index compared to the untreated control. The PSA level in the extract-treated groups (4.33 ± 0.24) showed a significant (p < 0.05) decrease compared to the untreated control (6.75 ± 0.32). Additionally, a dose-dependent significant (p < 0.05) reduction in testosterone concentrations of JTLEE-treated rats was observed. There was a significant (p < 0.05) elevation of HDL levels of rats treated with varying doses of the JTLEE (3.93 ± 0.16) compared to the untreated group (2.07 ± 0.23). Considering the above results, it could be concluded that JTLEE possesses an anti-BPH effect as observed in the reduction of prostate tissues and significant changes in other prostate indices.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1.Devlin CM, Simms MS, Maitland NJ. Benign prostatic hyperplasia – what do we know? BJU Int. 2021; 127(4): 389-399.
2.De Nunzio C, Ahyai S, Autorino R, Bachmann A, Bialek W, Briganti A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms: research priorities. Eur Urol. 2011; 60(6): 1205-1206.
3.Park WY, Song G, Park JY, Ahn KS, Kwak HJ, Park J. Ellagic acid improves benign prostate hyperplasia by regulating androgen signaling and STAT3. Cell Death Dis. 2022; 13(6): 554.
4.Fu X, Liu J, Liu D, Zhou Y, Guo Y, Wang Z. Glucose-regulated protein 78 modulates cell growth, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and oxidative stress in the hyperplastic prostate. Cell Death Dis. 2022; 13(1): 78.
5.Calogero AE, Burgio G, Condorelli RA, Cannarella R, La Vignera S. Lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia and erectile dysfunction: from physiology to clinical aspects. Aging Male. 2018; 21(4): 261-271.
6.Albisinni S, Biaou I, Marcelis Q, Aoun F, De Nunzio C, Roumeguère T. New medical treatments for lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia and future perspectives. BMC Urol. 2016; 16(1): 58.
7.Chughtai B, Forde JC, Thomas DDM, Laor L, Hossack T, Woo HH. Benign prostatic hyperplasia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016; 2: 16031.
8.Srivastava S, Virmani T, Haque MR, Alhalmi A, Al Kamaly O, Alshawwa SZ. Extraction, HPTLC analysis and antiobesity activity of Jatropha tanjorensis and Fraxinus micrantha on high-fat diet model in rats. Life. 2023; 13: 1248.
9.Danborno AM, Tarfa F, Toryila JE, Awheela EU, Shekarau VT. The effects of Jatropha tanjorensis aqueous leaf extract on haematological parameters in Wistar rats. J Afr Assoc Physiol Sci. 2019; 7: 133-137.
10.Ntak O, Ekpo E, State AI, State CR. Nutritional studies and antimicrobial activities of Jatropha tanjorensis leaves extracts against Escherichia coli isolates. Int J Innov Sci Res Technol. 2019; 4: 945-955.
11.Khanijo T, Jiraungkoorskul W. Review ergogenic effect of Long Jack, Eurycoma longifolia. Pharmacogn Rev. 2016; 10(20): 139-142.
12.Chhatre S, Nesari T, Somani G, Kanchan D, Sathaye S. Phytopharmacological overview of Tribulus terrestris. Pharmacogn Rev. 2014; 8: 45-51.
13.Yadav UCS, Baquer NZ. Pharmacological effects of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. in health and disease. Pharm Biol. 2014; 52: 243-254.
14.Ekeyi Y, Uchendu NO, Anaduaka EG, Ezeanyika LUS. Ethanol extract of Cassia sieberiana leaves ameliorates deviances associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats. All Life. 2021; 14(1): 473-483.
15.Lorke D. A new approach to practical acute toxicity testing. Arch Toxicol. 1983; 53: 275-287.
16.Trease GE, Evans WC. Pharmacognosy. 15th ed. London: Saunders Publishers; 2002. p. 42-44, 221-229, 246-249, 404-306, 331-332, 391-393.
17.Harborne JB. Textbook of phytochemical methods: a guide to modern techniques of plant analysis. London: Chapman and Hall Ltd; 1973. p. 49-188.
18.Al-Trad B, Aljabali A, Al Zoubi M, Shehab M, Omari S. Effect of gold nanoparticles treatment on the testosterone induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019; 14: 3145-3154.
19.Abo-Youssef AM, Afify H, Azouz AA, Abdel-Rahman HM, Abdel-Naim AB, Allam S. Febuxostat attenuates testosterone induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats via inhibiting JAK/STAT axis. Life Sci. 2020; 260: 118414.
20.Goldberg DM, Spooner RJ. Assay of glutathione reductase. In: Bergmeyer HV, editor. Methods of enzymatic analysis. 3rd ed. Vol 3. Deerfield Beach: Verlag Chemie; 1983. p. 258-265.
21.Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: an adaptation to a pragmatic gas. J Biol Chem. 1989; 264: 7761-7764.
22.Aebi HE. Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU, Bergmeyer J, Grassl M, editors. Methods of enzymatic analysis. 3rd ed. Florida: Weinheim Deerfield Beach; 1983. p. 273-285.
23.Wallin B, Rosengren B, Shertzer HG, Camejo G. Lipoprotein oxidation and measurement of thiobarbituric acid reacting substances formation in a single microtiter plate: its use for evaluation of antioxidants. Anal Biochem. 1993; 208: 10-15.
24.Tietz NW. Clinical guide to laboratory tests (ELISA). 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company; 1990. p. 932-933.
25.Albers JJ, Warmick GR, Cheng MC. Quantitation of high density lipoproteins. Lipids. 1978; 13: 926-932.
26.Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972; 18: 499-502.
27.Abell LL, Levey BB, Brodie BB, Kendall FE. Extraction of cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1952;195(1): 357-363.
28.Reitman S, Frankel S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957; 28: 56-63.
29.Babson AL, Greeley SJ, Coleman CM, Philips GE. Phenolphthalein monophosphate as a substrate for serum alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chem. 1966; 12(8): 482-490.
30.Drury RA, Wallington EA, Cameroun SR. Carleton’s histological techniques. New York: Oxford University Press; 1967. p. 1-420.
31.Komolafe CJ, Adetoyinbo II, Alao OF, Ogunsola FJ. Phytochemical analyses and antibacterial activities of Jatropha tanjorensis J. L. Ellis and Saroja leaves extract against clinical pathogens. Asian J Appl Chem Res. 2024; 15(5): 9-23.
32.Oboh G, Raddatz H, Henle T. Characterization of the antioxidant properties of hydrophilic extract of Jatropha tanjorensis leaves. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2009; 60(5): 1-12.
33.OECD. OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 4: health effects - test no. 423: acute oral toxicity - acute toxic class method. OECD Publishing; 2021.
34.Smith LA, Roberts AM, Chen Y. Feedback regulation of gonadal function by exogenous androgens. Reprod Biol. 2021; 44(2): 99-108.
35.Johnson M, Nguyen T. Testosterone-induced testicular atrophy: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Endocrinol Metab. 2022; 36(1): 12-22.
36.Clarkson J, Smith K, Turner R. 5α-Reductase inhibitors in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urol Rev. 2019; 45(3): 180-192.
37.Wang J, Zhao M, Li X. Protective effects of antioxidants on testicular function under androgen excess conditions. Front Pharmacol. 2023; 14: 112344.
38.Miller DP, Carter JL, Singh P. Androgen-driven prostate enlargement: pathophysiology and treatment strategies. J Androl. 2020; 41(5):450-459.
39.Traish AM, Hassani J, Guay AT. Mechanisms of 5α-reductase inhibitors in prostate disease. Clin Endocrinol. 2019; 90(1): 10-19.
40.Lee H, Park J, Kim S. Anti-inflammatory and androgen receptor modulatory effects of plant-derived compounds in prostate health. Phytomedicine. 2024; 99: 153940.
41.Kumar N, Singh A, Gupta P. Testosterone-induced prostatic hyperplasia and PSA elevation: molecular and clinical perspectives. Andrology. 2021; 9(1): 112-121.
42.Miyamoto H, Izumi K, Nakazawa H. PSA as a biomarker in prostate disease: recent advances and challenges. Prostate Int. 2022; 10(2): 85-92.
43.Kaufman KD, Olsen EA, Whiting D. The clinical efficacy of 5α-reductase inhibitors in benign prostatic hyperplasia: a comprehensive review. J Urol. 2023; 210(5): 1021-1030.
44.Brawer MK, Chen H, Gupta R. Dihydrotestosterone and prostate growth: mechanistic insights and clinical implications. Endocr Rev. 2020; 41(3): 250-270.
45.Li W, Chen Y, Wang Z. Natural compounds targeting androgen metabolism in benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review. Phytother Res. 2024; 38(1): 12–27.
46.Traish AM, Haider A, Haider KS, Doros G, Saad F. Testosterone and lipid metabolism. Int J Clin Pract. 2011; 65(4): 469-480.
47.Zhao S, Haider KS, Doros G. Androgen effects on hepatic lipid metabolism and cardiovascular health. Front Endocrinol. 2022; 13: 815.
48.Fahed G, Chen H, Gupta R. Testosterone and cardiovascular risk: a review. Clin Lipidol. 2021; 16(4): 371-386.
49.Chen X, Singh A, Gupta P. Effects of finasteride on lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity in androgen-induced metabolic dysregulation. Endocrinol Metab. 2023; 38(1): 15-26.
50.Ghasemzadeh A, Raddatz H, Henle T. Plant extracts modulating lipid metabolism in experimental models. Front Pharmacol. 2020; 11: 587.
51.Zhang Y, Olsen EA, Whiting D. Role of natural compounds in lipid metabolism regulation: recent advances. Nutr Metab. 2023; 20(1): 12.
52.Morgentaler A. Androgen therapy and lipid metabolism: reassessing the evidence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021; 106(7): 1800-1807.
53.Rohatgi A, Khera A, Berry JD, Givens EG, Ayers CR, Wedin KE, Neeland IJ, Yuhanna IS, Rader DR, de Lemos JA, Shaul PW. HDL cholesterol efflux capacity and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371(25): 2383-2393.
54.Choudhary N, Wang X, Ma Y, Xu Q, Shikov AN, Pozharitskaya ON, et al. Flavonoids and saponins in cardiovascular protection: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Phytother Res. 2022; 36(2): 567-579.
55.Smith A, Johnson R. Androgen excess and oxidative stress in prostate pathophysiology. Front Endocrinol. 2021; 12: 723456.
56.Wang L, Zhou X, Li Q. Testosterone-induced oxidative stress: mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2022; 533: 111282.
57.Patel R, Desai S, Shah N. Antioxidant therapy in BPH: clinical and experimental perspectives. Int J Urol. 2020; 27(5): 409-416.
58.Kim S, Park J, Choi Y. Finasteride and antioxidant status in experimental BPH models. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023; 26(1): 14-22.
59.Chen Y, Zhang H, Li X. Phytochemicals and antioxidant activity: dose-dependent effects in prostate health. Phytother Rev. 2024; 38(1): 54-66.
60.Liu F, Wang J, Huang Z. Dose-dependent effects of herbal extracts on antioxidant enzymes in BPH rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023; 2023: 9876543.
61.Zhang Y, Huang M. Catalase regulation in oxidative stress and prostate diseases. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(7): 1345.
62.Kumar A, Gupta P. Oxidative stress markers in benign prostatic hyperplasia: role of lipid peroxidation. Urol Ann. 2021; 13(3): 182-190.
63.Alvarez R, Smith M, Lee J. Testosterone-induced oxidative stress and prostatic damage: mechanisms and interventions. J Androl Res. 2023; 45(2): 123-135.
64.Ojo OO, Adebayo OO, Akinyemi A. Testosterone propionate-induced liver injury and oxidative stress in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022; 438: 115869.
65.Zhang L, Chen W, Li Q. Biomarkers of hepatic injury in experimental models. Front Pharmacol. 2023; 14: 1125607.
66.Alarcon-Aguilar FJ, Rodriguez-Castaneda A, Martinez-Diaz F. Androgen-induced liver injury: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Liver Int. 2021; 41(9): 2041-2052.
67.Singh V, Kumar R, Yadav D. Androgens and liver health: insights into biochemical pathways. Endocr Rev. 2022; 43(2): 189-207.
68.Chen Y, Wu M. Protective effects of plant extracts on hepatic oxidative stress in animal models. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021; 278: 114308.
69.Rahman MA, Islam MS, Akter R. Hepatoprotective role of herbal antioxidants in androgen-induced liver damage. Phytomedicine. 2023; 112: 154678.
70.Gupta R, Sharma S. Differential sensitivity of liver enzymes in hepatotoxicity assessment. Toxicol Rep. 2023; 10: 134-142.
71.Mishra A, Patel N, Singh S. Serum transaminases and alkaline phosphatase as biomarkers of liver function. Clin Biochem. 2024; 101: 45-53.
72.Shappell SB, Thomas GV, Roberts RL, Herbert R, Ittmann MM, Rubin MA. Prostate histopathology in rodent models: a comparative review. Toxicol Pathol. 2021; 49(2): 235-248.
73.Kwon J, Jeong JH, Kim SY. Histopathological features and molecular markers in benign prostatic hyperplasia: insights from rat models. J Pathol Transl Med. 2022; 56(3): 168-176.
74.Yusuf MA, Ibrahim NDG, Shuaibu MN. The ameliorative role of medicinal plant extracts in prostatic hyperplasia models: a review of current evidence. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13: 890921.
75.Chen Y, Huang C, Wu X. Phytotherapeutic potential of Justicia species: anti-inflammatory and prostatic protective effects. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023; 310: 116632.
76.Yamada Y, Fujimoto N. Corpora amylacea in the prostate: significance in physiology and pathology. Prostate. 2020; 80(11): 861-870.
77.Odoh UE, Owoh CC, Obi PE, Chukwuma MO, Agubata CW, Odoh LC. Pharmacognostic profile and anti-hyperglycemic activity of Jatropha tanjorensis Linn (Euphorbiaceae) leaf on alloxan-induced hyperglycemic rats. J Adv Med Pharm Sci. 2023;25(5):30-42.