Hepatoprotective Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. in Severe Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity: High-Dose and Dose-Response Study
Main Article Content
Abstract
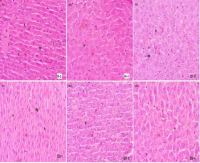
Liver disease remains a significant global health challenge, and despite progress in modern medicine, there is no pharmacological treatment that provides full protection or regeneration of liver tissue. Paracetamol, although widely used as an analgesic and antipyretic, is known to cause liver toxicity in overdose conditions. The objective of this research was to assess the hepatoprotective potential of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. extract in severe hepatotoxicity induced by high-dose paracetamol (2000 mg/kg BW), a dosage rarely explored in previous studies. The experimental rats were randomly divided into five distinct groups: a negative control, a positive control, and three treatment groups receiving Hibiscus sabdariffa L extract at 300, 550, and 1000 mg/kg BW, respectively. Histopathological analysis showed that the extract at 1000 mg/kg BW offered the highest level of protection, with minimal signs of hemorrhage, necrosis, or apoptosis, and improved hepatocellular morphology. The hepatoprotective effect of the extract may be attributed to the presence of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, particularly anthocyanins and polyphenols, which have been shown to enhance antioxidant enzyme activity and reduce oxidative stress. The present results reinforce the possibility that Hibiscus sabdariffa L. may serve as a promising natural therapeutic agent that could offer hepatoprotective effect against drug-induced liver injury.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1.Ramachandran A and Jaeschke H. Mechanisms of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and their translation to the human pathophysiology. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2020; 8(2):112–122.
2.Kaplowitz N. Drug-induced liver injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017; 3(1):1–12.
3.Bernal W, Wendon J, Williams R. Acute liver failure. N Engl J Med. 2015; 369(26):2525–2534.
4.Yoon E, Babar A, Choudhary M, Kutner M, Pyrsopoulos N. Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: A comprehensive update. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2016; 4(2):131–142.
5.Hirunpanich V, Utaipat A, Morales NP, Bunyapraphatsara N, Sato H, Herunsalee A. Antioxidant and hypolipidemic activities of aqueous extract from the dried calyx of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. in hypercholesterolemic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016; 103(2):252–260.
6.Olatunji LA and Afolayan AJ. Hibiscus sabdariffa calyx extract modulates lipid metabolism and improves antioxidant status in diabetic rats. J Diabetes Res. 2018; 2018:1–7.
7.Nwozo SO, Oyinloye BE, Adeleke GE. Effect of aqueous extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa on ethanol-induced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in rats. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2015; 2015:1–7.
8.Hamza RZ and Amin MM. Comparative protective effects of Ginkgo biloba and Hibiscus sabdariffa against hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity induced by ethanol in rats. J Toxicol. 2017; 2017:1–10.
9.Jaeschke H, McGill MR, Ramachandran A. Oxidant stress, mitochondria, and cell death mechanisms in drug-induced liver injury: Lessons learned from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Rev. 2014; 44(1):88–106.
10.Ologundudu A, Obi FO, Ezeani NE. The hepatoprotective potentials of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. anthocyanins on 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine-induced oxidative stress in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016; 184:84–89.
11.Mohamed S, Hassan HA, El-Beshbishy HA. Antioxidant and antiapoptotic effects of saffron extract in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. J Intercult Ethnopharmacol. 2015; 4(1):8–13.
12.Al-Qabba MM, El-Metwally AE, Farag NE, Abd-El-Kareem MS, Soliman WE. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa extract against ibuprofen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2019; 42(6):576–584.
13.Muhammad NO, Fajilade LA, Ajiboye BO, Oyeniyi BO. Protective effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in rats. J Toxicol. 2020; 2020:1–8.
14.Guo H, Ling W, Wang Q, Liu C, Hu Y, Xia M, Zhang Y. Effect of anthocyanin-rich extract from black rice on hepatic antioxidant capacity and lipid peroxidation in rats. Food Nutr Res. 2009; 53:1–8.
15.Obouayeba AP, Dasse SR, Djaman AJ, N'Guessan JD, Guede NZ. Assessment of hepatoprotective activity of polyphenol-rich fractions of Cajanus cajan leaves in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in rats. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2014; 4(6):442–446.
16.Sharma P and Paliwal R. Chemopreventive potential of curcumin and quercetin against benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung carcinogenesis in mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2012; 64(7–8):471–478.
17.Falodun A, Siraj R, Choudhary MI. GC-MS insecticidal leaf essential oil of P. staudtii Hutch and Dalz (Icacinaceae). Trop J Pharm Res. 2009; 8(2):139–143.
18.Okolie NP, Falodun A, Oluseyi D. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of root extract of pepper fruit (Dennetia tripetala), and its potential for the inhibition of lipid peroxidation. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014; 11(3):221–227. doi:10.4314/ajtcam.v1/1i3.31