Antioxidant and Toxicological Evaluation of Vigna subterranea Seed (Bambara Nut) Fractions on High-Fat Diets-Induced Oxidative Stress in Male Wistar Rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
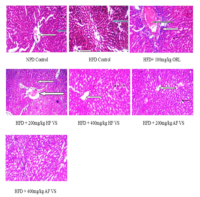
High-fat diets (HFD) produce free radicals that trigger oxidative stress, increasing the risk of several health challenges. Medicinal plants have shown good antioxidant properties that ameliorate oxidative stress related diseases. This study examined how the hexane (HF) and aqueous (AF) fractions of Vigna subterranea (VS) reduce oxidative stress caused by HFD in Wistar rats. A total of 49 adult male Wistar rats were placed into seven groups of seven each. Group 1 (normal control) received standard feed and water, while groups 2–7 were fed HFD for 12 weeks. Afterwards, treatments were given daily for 4 weeks as: Group 2 (HFD + water), Group 3 (HFD + 100 mg/kg orlistat), Groups 4 and 5 (HFD + 200/400 mg/kg HF), and Groups 6 and 7 (HFD + 200/400 mg/kg AF). Various biochemical, haematological, oxidative stress markers, and tissue analyses (liver and kidney) were conducted using standard techniques. Results showed that both HF and AF significantly (p<0.05) reduced food intake, body weight, cholesterol levels, AST, ALT, creatinine, urea, and malondialdehyde (MDA), while increasing SOD, CAT, GSH and HDL. No liver or kidney inflammation was observed. These findings suggest that Vigna subterranea extracts may help reduce high serum cholesterol, MDA, and tissue damage without adverse effects, supporting needs for additional studies.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1.Chaudhary P, Janmeda P, Docea AO, Yeskaliyeva B, Abdull Razis AF, Modu B. Oxidative stress, free radicals and antioxidants: potential crosstalk in the pathophysiology of human diseases. Front Chem. 2023;11:1-24.doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1158198
2.Medrano-Macías J, Flores-Gallegos AC, Nava-Reyna E, Morales I, Tortella G, Solís-Gaona S. Reactive oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur species (RONSS) as a metabolic cluster for signaling and biostimulation of plants: An overview. Plants. 2022;11(23):1-27.doi: 10.3390/plants11233203.
3.Martemucci G, Costagliola C, Mariano M, D'andrea L, Napolitano P, D'Alessandro AG. Free radical properties, source and targets, antioxidant consumption and health. Oxygen. 2022;2(2):48–78.doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2020006
4.Jomova K, Raptova R, Alomar SY, Alwasel SH, Nepovimova E, Kuca K, Valko M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging. Arch Toxicol. 2023;97(10):2499–2574.doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03562-9
5.Jomova K, Alomar SY, Alwasel SH, Nepovimova E, Kuca K, Valko M. Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants. Arch Toxicol. 2024;98(5):1323–1367.doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03696-4.
6.Sharifi-Rad M, Anil Kumar NV, Zucca P, Varoni EM, Dini L, Panzarini E, Rajkovic J, Tsouh Fokou PV, Azzini E, Peluso I, Prakash Mishra A, Nigam M, El Rayess Y, Beyrouthy ME, Polito L, Iriti M, Martins N, Martorell M, Docea AO, Setzer WN, Calina D, Cho WC, Sharifi-Rad J. Lifestyle, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: back and forth in the pathophysiology of chronic diseases. Front Physiol. 2020;11:1-21: doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.00694
7.Piko N, Bevc S, Hojs R, Ekart R. The role of oxidative stress in kidney injury. Antioxidants. 2023;12(9):1-13.doi: 10.3390/antiox12091772
8.Wongchitrat P, Klosen P, Pannengpetch S, Kitidee K, Govitrapong P, Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya C. High-fat diet-induced plasma protein and liver changes in obese rats can be attenuated by melatonin supplementation. Nutr Res. 2017;42:51–63.doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2017.04.011.
9.Bhattacharyya A, Chattopadhyay R, Mitra S, Crowe SE. Oxidative stress: An essential factor in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal mucosal diseases. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(2):329–354.doi: 10.1152/physrev.00040.2012.
10.Carresi C, Mollace R, Macrì R, Scicchitano M, Bosco F, Scarano F, Coppoletta AR, Guarnieri L, Ruga S, Zito MC, Nucera S, Gliozzi M, Musolino V, Maiuolo J, Palma E, Mollace V. Oxidative stress triggers defective autophagy in endothelial cells: role in atherothrombosis development. Antioxidants. 2021;10(3)387-395.
11.Roginskaya M, Razskazovskiy Y. Oxidative DNA damage and repair: mechanisms, mutations, and relation to diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(8):1-3.doi: 10.3390/antiox12081623.
12.Poetsch AR. The genomics of oxidative DNA damage, repair, and resulting mutagenesis. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020;18:207–219.doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.12.013.
13.Kesh S, Sarkar D, Manna K. High-fat diet-induced oxidative stress and its impact on metabolic syndrome: A review. 2016;9:38–43.doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56538-0.
14.Lasker S, Rahman MM, Parvez F, Zamila M, Miah P, Nahar K, Kabir F, Sharmin SB, Subhan N, Ahsan GU, Alam MA. High-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome and oxidative stress in obese rats are ameliorated by yogurt supplementation. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1-15.doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56538-0
15.Stéphane FFY, Jules BKJ, Batiha GES, Ali I, Bruno LN, El-Saber Batiha G, Ali I, Ndjakou Bruno L. Extraction of bioactive compounds from medicinal plants and herbs. In: Nat Med Plants. 2022: 22(9)1-41 doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.98602
16.Clemence M, Rene K, Jean-Louis EO. Subchronic toxicity of Crinum jagus extracts on Wistar rats. J Pharm Med Res. 2021;6(1):117–120.doi:10.30799/jpmr.054.21060102
17.Ramatsetse KE, Ramashia SE, Mashau ME. A review on health benefits, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea). Int J Food Prop. 2023;26(1):91–107.doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4059.
18.Majola NG, Gerrano AS, Shimelis H. Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea [L.] Verdc.) production, utilisation and genetic improvement in Sub-Saharan Africa. Agronomy. 2021;11(7):1-17.doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11071345
19.Oluwole O, Oluwole O, Nwachukwu Nicholas-Okpara V, Elemo G, Adeyoju O, Deborah I. Maryam O.A. Medicinal uses, nutraceutical potentials and traditional farm production of Bambara beans and pigeon pea. Glob J Epidemiol Public Health. 2021;6:41–50. doi:10.12974/2313-0946.2021.06.01.3
20.Okafor JNC, Jideani VA, Meyer M, Le Roes-Hill M. Bioactive components in Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea [L.] Verdc.) as a potential source of nutraceutical ingredients. Heliyon. 2022;8(3):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09024.
21.Adedayo, B.C., Anyasi, T.A., Taylor, M.J.C. Phytochemical composition and antioxidant properties of methanolic extracts of whole and dehulled Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea) seeds. Sci Rep. 2024.11(1):1-11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93525-w.
22.Hostettmann K, Marston A, Hostettmann M. Separation strategy and combination of methods. In: Hostettmann K, Marston A, Hostettmann M, editors. Preparative Chromatography Techniques: Applications in Natural Product Isolation. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 1998. p. 230–240.
23.Test No. 420: Acute Oral Toxicity - Fixed Dose Procedure. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4, OECD Publishing, Paris, 2002.ENV/JM/MONO(2001)(4):1-24 doi.org/10.1787/9789264070943-en.
24.EL-Kamali HH, Osman GA. GC/MS Analysis of Chemical Compounds Soluble in n-Hexane and Petroleum Ether from Trigonella foenum-graecum Seeds. Asian J Biol Sci. 2023;17(4):640–648.doi.org/10.3923/ajbs.2024.640.648
25.Anyanwu GO, Iqbal J, Khan SU, Zaib S, Rauf K, Onyeneke CE, Ojo OO, Nisar-Ur-Rahman. Antidiabetic activities of chloroform fraction of Anthocleista vogelii Planch root bark in rats with diet- and alloxan-induced obesity-diabetes. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;229:293–302.doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.10.021.
26.Banerjee A, Das D, Paul R, Roy S, Bhattacharjee A, Prasad SK, Banerjee O, Mukherjee S, Maji BK. Altered composition of high-lipid diet may generate reactive oxygen species by disturbing the balance of antioxidant and free radicals. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;31(3):141-156
27.Megwas AU, Njoku O, Alabi OJ, Airaodion AI. Ameliorative potential of Bambara nuts against acute ethanol-induced oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Int. J. Res 2021;8(2):115-129.
28.Ponnampalam EN, Kiani A, Santhiravel S, Holman BWB, Lauridsen C, Dunshea FR. The importance of dietary antioxidants on oxidative stress, meat and milk production, and their preservative aspects in farm animals: antioxidant action, animal health, and product quality invited review. Animals. 2022;12(23):1-45.doi.org/10.3390/ani12233279
29.Abdulmumin T, Yunusa A, Alhassan A, Muhammad I, Dalhatu M, Amina L, Bichi SA, Sarki SI. Amino acid evaluation and GC-MS analysis of Bambaranut (Vigna subterranea [L.] Verdc.). Malays. J. Chem. 2020;22(1):78-86.
30.Adebiyi JA, Njobeh PB, Adebo OA, Kayitesi E. Metabolite profile of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea) and dawadawa (an African fermented condiment) investigation using gas chromatography high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC-HRTOF-MS). Heliyon. 2021;7(4):1-10.doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06666.
31.Mazumder K, Nabila A, Aktar A, Farahnaky A. Bioactive variability and in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity of unprocessed and processed flour of nine cultivars of Australian lupin species: A comprehensive substantiation. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(4):1-23.doi: 10.3390/antiox9040282.
32.Guerrero RV, Vargas RA, Petricevich VL. Chemical compounds and biological activity of an extract from Bougainvillea x buttiana (var. rose) Holttum and Standl. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2017;9(3):42-46. doi:10.22159/ijpps.2017v9i3.16190
33.Gawron-Skarbek A, Guligowska A, Prymont-Przymińska A, Nowak D, Kostka T. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant 33.impact of dietary fatty acids in cardiovascular protection in older adults may be related to vitamin C intake. Antioxidants. 2023;12(2):1-12.doi: 10.3390/antiox12020267
34.Liang H, Jiang F, Cheng R, Luo Y, Wang J, Luo Z, Li M, Shen X, He F. A high-fat diet and high-fat and high-cholesterol diet may affect glucose and lipid metabolism differentially through gut microbiota in mice. Exp Anim. 2021;70(1):73–83.doi: 10.1538/expanim.20-0094.
35.Megwas AU, Akunne PN, Oladosu NO, Alabi OJ, Njoku OC, Airaodion AI. Effect of Bambara Nut Consumption on Blood Glucose Level and Lipid Profile of Wistar Rats. Int. J. Res. Rep. Hematol. 2021;4(1):30-41. Article no.IJR2H.66256
36.Abigail A, Godwin N, Uduakobong B, Luka C. Assessment of antihyperglycemic effect of nut fractions of Vigna subterranea on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Res. Publ. Rev 2023;4(6):3360–3371.www.ijrpr.com ISSN 2582-7421
37.Halliwell B. Understanding mechanisms of antioxidant action in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 ;25(1):13-33.doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00645-4
38.Zhang H, Song C, Yan R, Cai H, Zhou Y, Ke X. High-fat diet accelerates hepatic fatty acids synthesis in offspring male rats induced by perinatal exposure to nonylphenol. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021;22(1):21-22. doi: 10.1186/s40360-021-00492-z.
39.Dos Santos Lacerda D, Garbin de Almeida M, Teixeira C, De Jesus A, Da Silva Pereira Júnior É, Martins Bock P. Biochemical and physiological parameters in rats fed with high-fat diet: The protective effect of chronic treatment with purple grape juice (Bordo variety). Beverages. 2018;4(4):1-13.doi:10.3390/beverages4040100
40.Airaodion AI, Akunne PN, Njoku OC, Oladosu NO, Megwas AU. Effect of Bambara Nut on Hepatic Biomarkers of Wistar Rats. Int Res J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;4(1):26–38. Article no.IRJGH.67056
41.Njoku O. Effect of Bambara Nut on Hepatic Biomarkers of Wistar Rats. Int Res J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;4(1):26-38. https://journalirjgh.com/index.php/IRJGH/article/view/49
42.Gf M, A K, Ap Y. Effects of metabolic syndrome on blood cells to Wistar rats. JDMDC. 2018;5(6):222-225.doi:10.15406/jdmdc.2018.05.00170
43.Yang L, Shi F, Cao F, Wang L, She J, He B, Xu X, Kong L, Cai B. Neutrophils in tissue injury and repair: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Med Comm. 2025 Apr 21;6(5):1-18.doi: 10.1002/mco2.70184.
44.Qi Z, Hu L, Zhang J, Yang W, Liu X, Jia D, Yao Z, Chang L, Pan G, Zhong H, Luo X, Yao K, Sun A, Qian J, Ding Z, Ge J. PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9) enhances platelet activation, thrombosis, and myocardial infarct expansion by binding to platelet CD36. Circul. 2021;143(1):45-61.doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046290.
45.Saputri FC, Azmi NU, Puteri MU, Damayanti, Novita V, Marisi G, Oktavira E, Sari AN, Ronaningtyas K, Herawati E. High-fat diet enhances platelet activation and is associated
46.with proprotein convertase subtilisin Kexin 9: An animal study. Nutri. 2023;15(20):1-14. doi: 10.3390/nu15204463
47.Shabalala SC, Johnson R, Basson AK, Ziqubu K, Hlengwa N, Mthembu SXH, Mabhida SE, Mazibuko-Mbeje SE, Hanser S, Cirilli I, Tiano L, Dludla PV. Detrimental effects of lipid peroxidation in type 2 diabetes: Exploring the neutralizing influence of Product Development Program, Institute of Agricultural Research and Training, Obafemi Awolowo University, Nigeria, Olanipekun OT, Omenna EC, Kenaf and Jute Improvement Program, Institute of Agricultural Research and Training, Obafemi Awolowo University, Nigeria, Adeniyi GA, Department of Family Nutrition and Consumer Sciences, Faculty of Agriculture, Obafemi Awolowo University, Nigeria. Effect of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea) consumption on biomarkers of oxidative stress in alloxan-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Res J Food Sci Nutr. 2019;4(3):65–72. Doi.org/10.31248/RJFSN2019.066
48.Kalra A, Yetiskul E, Wehrle CJ. Physiology, Liver. In: StatPearls 2023. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; PMID: 30571059.
49.Ogobuiro I, Tuma F. Physiology, renal. In: StatPearls 2023, StatPearls Publishing,Treasure Island. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30855923/
50.Gonçalves RV, Costa AMA, Grzeskowiak L. Oxidative stress and tissue repair: Mechanism, biomarkers, and therapeutics. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;21(27):1-3.Doi: 10.1155/2021/6204096.
51.Kocyigit E, Kocaadam-Bozkurt B, Bozkurt O, Ağagündüz D, Capasso R. Plant toxic proteins: Their biological activities, mechanism of action and removal strategies. Toxins (Basel). 2023;15(6):356. DOI: 10.3390/toxins15060356